Xueyun Qian, Klaus Wölfel, Jean-Paul Smets, Jingjing XU, Alain Takoudjou, Mathias Riechert, Ni Yan |
How to evaluate the answers from the interview ( read before you interview the company)
How to fill the Configuration Questionnaire
This visual guide is part of a collection of documents created by the One Student One ERP (OSOE) project in collaboration with Institut Mines Telecom, Telecom Bretagne, Dresden University of Technology and the South Westfalia University of Applied Sciences. It can be used to teach modern ERP theory and practice to undergraduate students or professionals.
Copyright: You are free to copy, distribute, display, and perform the work under the following conditions: you must attribute the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor; you may not use this work for any commercial purposes including training, consulting, advertising, self-advertising, publishing, etc.; you may not alter, transform, or build upon this work. For any reuse or distribution, you must make clear to others the license terms of this work. Any of these conditions can be waived if you get permission from the copyright holder through a commercial license or an educational license. For more information, contact info@nexedi.com
Agenda
- How to provide high quality answers
- Question descriptions
Now we will focus on how to execute the interview and evaluate the answers we get from the interview. This tutorial will show you what constitutes a good answer, and discuss some questions in details.
What is a good answer?

In order to provide high quality answers, the term "high quality answer" has to be defined in the context of the questionnaire. It is important to always provide the answers in full sentences, avoiding bullet lists. This results in more context information being available for later analysis. Using clear and simple language helps condensing information on explicit and meaningful sentences.
Executives often tend to describe the organization's situation in rather general statements. So please make sure to get explicit processes and cases.
What is a bad answer?
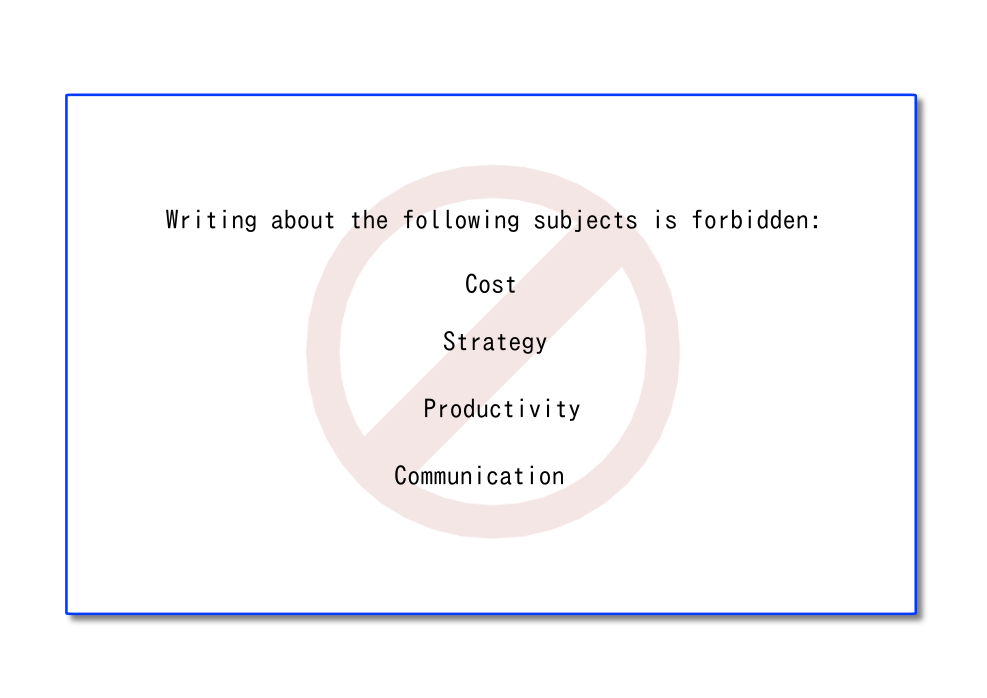
Here are the 4 terms frequently used by executives to hide the fact that they are not able to define what they precisely expect from an ERP: cost, strategy, productivity and communication.Those terms are forbidden subjects in this lecture. In other contexts, they could be useful terms. But here, they are reallly not.
For example, caring too much about specific way of computing a cost will have no impact on being able to deliver products in time. Cost does not even have any impact on cash, except very indirectly through the ability to obtain a bank loan by producing financial reports based on a cost formula that maximises EBITDA. This is not the role of an ERP, but of an external reporting system. This external reporting system needs nothing else but accurate data extracted from the ERP.
About strategy, executives often mention this word to hide the fact that they have no actual priorities for their ERP implementation.
Productivity - sometimes mentioned as efficient user interface - is also a way to escape from defining clear goals in terms of quantitative management. Real productivty derives from automation: an executive who has clear goals with thus explain how he plans to change organisation with the ERP and which part can be automated.
Communication is the last forbidden word. It refers often to the idea of the right information at the right time - which is not a bad idea - but it can only be achieved in an ERP and possibly with any management software by defining organisation processes of which the side effect is to bring that right information at the right time to the right person. We thus forbid this work too in order to ensure that executives define that organisation process.
What is a good answer - Example
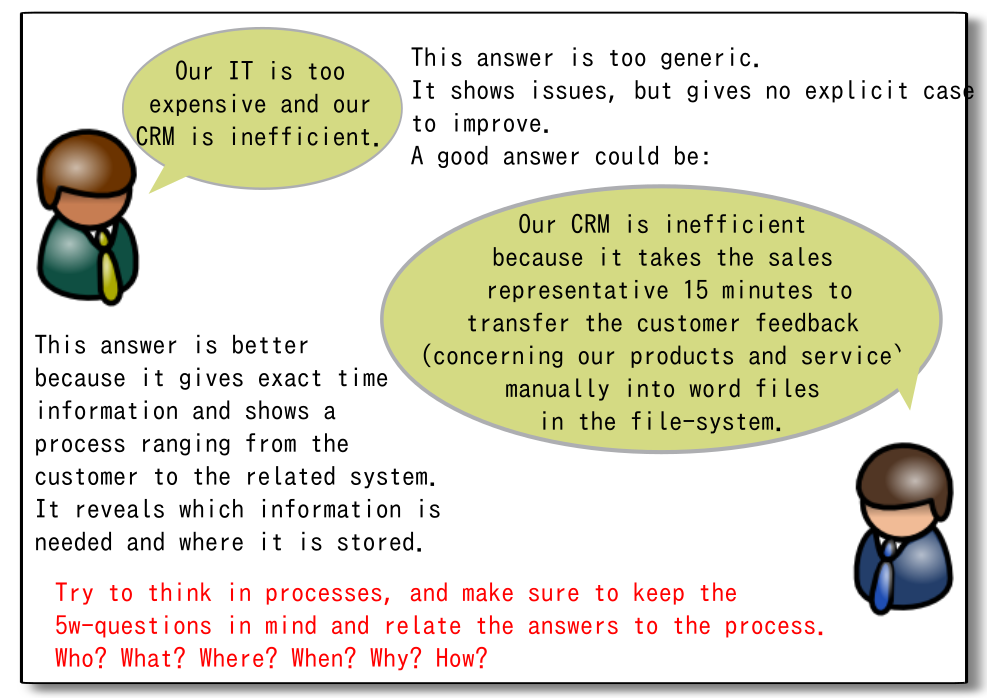
The first answer example shown is too generic. It shows issues (cost, inefficiency), but it gives no explicit case to improve. To make the answer more explicit, asking the 6-w questions (Who? What? Where? When? Why? How?) can help analyse the relevant facets of the described process. Still the aim is to get a cohesive description of the process.
Question description
The following slides describe how to answer the questions about the company in detail. For each question a number of sub questions is provided. Provide explicit processes rather then general statements.
Question description

This question aims at identifying the output of the company, encompassing products, services or trading goods. Give the highest possible detail on what is sold (with hierarchy), where it is sold and to whom it is sold.
It is also possible to use ERP5 only for a department or special tasks within the organisation. In this case both the company's (generally) and the department's (detailed) products have to be documented.
Question description
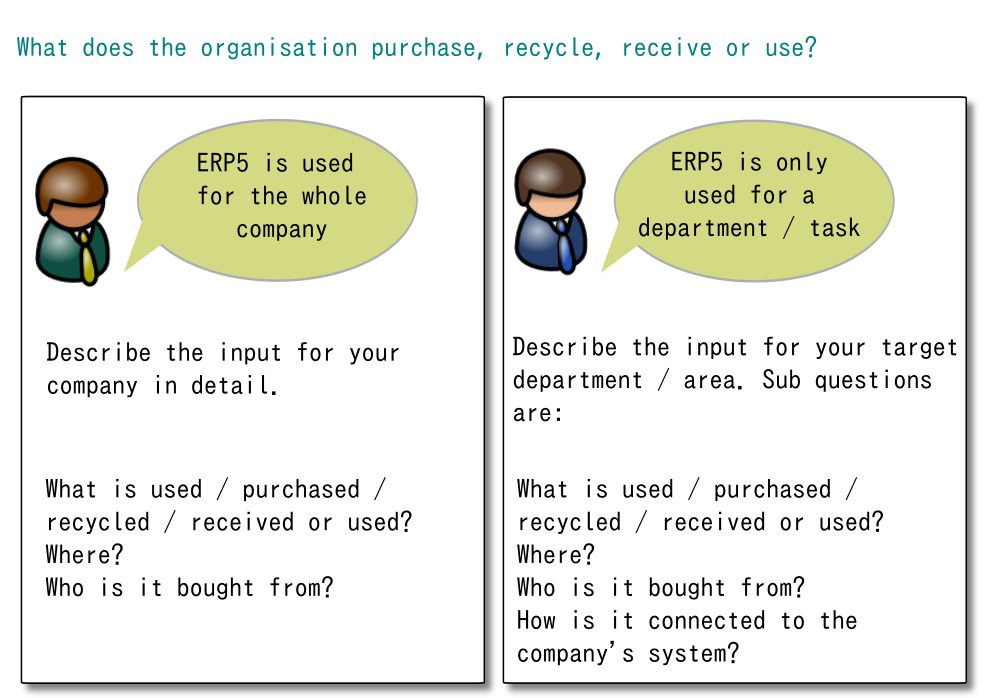
This question aims at identifying the input for the organisation. The input can be used, purchased or recycled by the company.
If you only use ERP5 for a department or special task in the organisation, make sure to describe the inputs explicitly for both the whole company and the department ERP5 is used in.
Question description
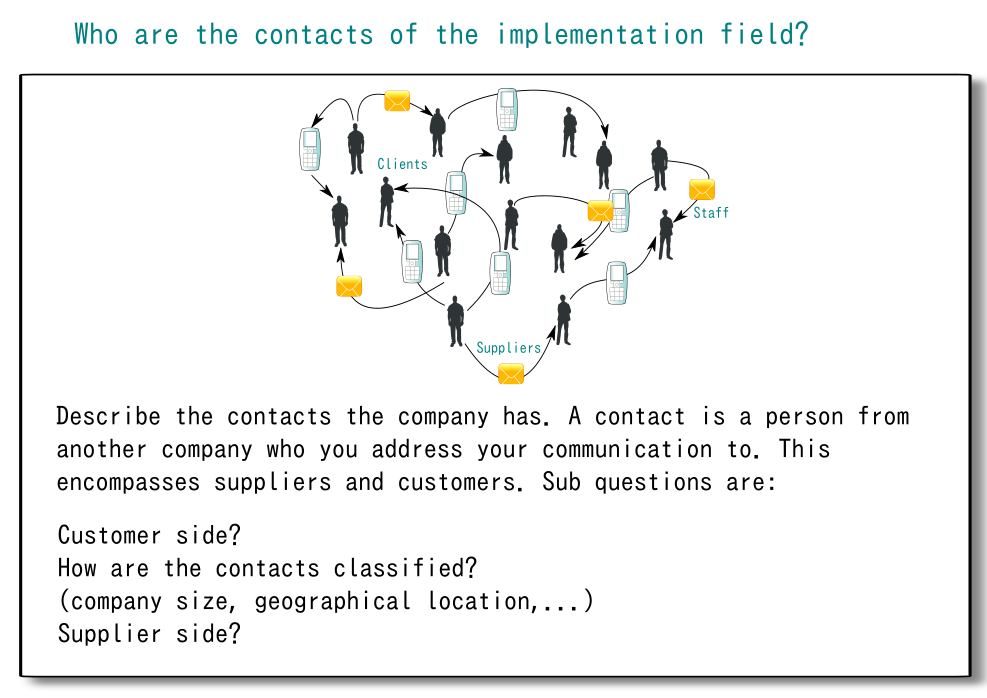
Provide details about all the contacts the company has. Both suppliers and customers have contact persons with whom your company communicates. The goal is to get informations about the categories role, region, group and function so to analyse the contacts regarding these categories.
Analyse the company's contacts on the customer and supplier side. Your company may have other contact roles, so think of possible classifications (size, location,...?). It is possible that contacts are organized in hierarchies (like in large companies with many subsidiaries).
Question description

The aim of this question is to get information about the employees skills for the skill category. Ensure to take both skills inside and outside your company into consideration. It is possible to directly ask for the provided skill categories, but be aware that the company might have a individual skill structure. Make sure to list key and unique skills that are specific for the company you're analysing.
Question description
This question aims at identifying a process the company is handling successful. Ensure to describe an explicit process with humans interacting. Give as much detail as possible about the time span for each sub-process and point out why this is a benefit for the company.
Additionally asking the 5-w questions helps ensuring that all facets are considered.
Question description

This question aims at identifying a process the company is handling wrongly. Describe an explicit process with humans interacting. Give as much detail as possible about the time span for each sub-process and point out what could be improved.
Additionally asking the 6-w questions helps ensuring that all facets are considered.Question description
This question aims at identifying possible solutions based on the improvement potential.
Describe an explicit process with humans interacting. Give as much detail as possible about the time span for each sub-process and point out why it is an improvement.
Thank You
- Rapid.Space
- 147 Rue du Ballon
- 59110 La Madeleine
- France
- +33629024425
- contact (@) rapid.space
For more information, please contact Jean-Paul, CEO of Rapid.Space (+33 629 02 44 25).